ラズベリーパイPico WとモータドライバでDCモータを動かしてみよう
ラズベリーパイPico WでDCモータを動かしてみます。
DCモータについてはマイクロビットとモータドライバでDCモータを動かしてみようをご覧ください。
ラズベリーパイPico WでDCモータを動かす時もモータドライバを利用します。

今回はKitronik製のRaspberry Pi Pico用モータードライバ基板 を利用します。
Raspberry Pi Pico用モータードライバ基板 — スイッチサイエンス

ラズベリーパイPico WHを購入し、

このようにラズベリーパイPico Wをモータードライバと接続して使用します。
一度モータードライバと繋げたら、ラズベリーパイPico Wを外すのは難しいので、モータドライバ専用のラズベリーパイPico Wを購入することをおすすめします。
上記の内容を踏まえて、今回使用するものを挙げます。

ラズベリーパイPico W + モータドライバ × 1
GeekServo 9G Motor-Red × 1
GeekServo 9G Motor-Red — スイッチサイエンス
単三電池2本 スイッチ付き電池ボックス × 1
単三電池2本 スイッチ付き電池ボックス — スイッチサイエンス
ジャンパワイヤ(オス〜オス) × 2
単三電池 × 2
※上の写真では単三電池 × 4のものを使用しています
※今回のコードでDCモータの動作が悪かった時は単三電池 × 4を試してみましょう
上記の各パーツを
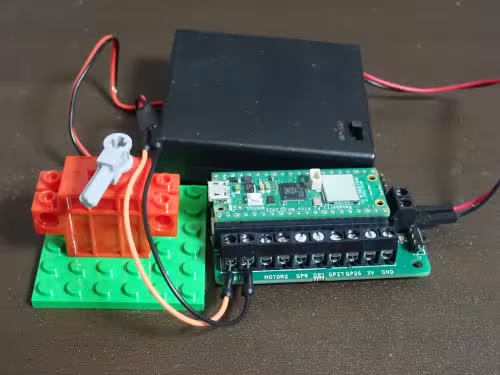
のように繋ぎます。
※繋ぎ方は上記のマイクロビットとモータドライバでDCモータを動かしてみようと同様の方法になります。
それでは早速コードを書いてみます。
ラズベリーパイPico Wではライブラリを読み込んでコードを作成するのが簡単なので、モータドライバ用のクラスを利用することにします。
下記URLを開き、エディタ(Thonny)にコードをペーストしPicoMotorDriver.pyというファイル名でラズベリーパイPico Wに保存します。
一応必要箇所を転機しておきます。
import machine
import utime
class KitronikPicoMotor:
def motorOn(self,motor, direction, speed):
#cap speed to 0-100%
if (speed<0):
speed = 0
elif (speed>100):
speed=100
#convert 0-100 to 0-65535
PWM = int(speed*655.35)
if motor == 1:
if direction == "f":
self.motor1Forward.duty_u16(PWM)
self.motor1Reverse.duty_u16(0)
elif direction == "r":
self.motor1Forward.duty_u16(0)
self.motor1Reverse.duty_u16(PWM)
else:
raise Exception("INVALID DIRECTION") #harsh, but at least you'll know
elif motor == 2:
if direction == "f":
self.motor2Forward.duty_u16(PWM)
self.motor2Reverse.duty_u16(0)
elif direction == "r":
self.motor2Forward.duty_u16(0)
self.motor2Reverse.duty_u16(PWM)
else:
raise Exception("INVALID DIRECTION") #harsh, but at least you'll know
else:
raise Exception("INVALID MOTOR") #harsh, but at least you'll know
#To turn off set the speed to 0...
def motorOff(self,motor):
self.motorOn(motor,"f",0)
def step(self,direction, steps, speed =20, holdPosition=False):
if(direction =="f"):
directions = ["f", "r"]
coils = [1,2]
elif (direction == "r"):
directions = ["r", "f"]
coils = [2,1]
else:
raise Exception("INVALID DIRECTION") #harsh, but at least you'll know
while steps > 0:
for direction in directions:
if(steps == 0):
break
for coil in coils:
self.motorOn(coil,direction,100)
utime.sleep_ms(speed)
steps -=1
if(steps == 0):
break
#to save power turn off the coils once we have finished.
#this means the motor wont hold position.
if(holdPosition == False):
for coil in coils:
self.motorOff(coil)
#Step an angle. this is limited by the step resolution - so 200 steps is 1.8 degrees per step for instance.
# a request for 20 degrees with 200 steps/rev will result in 11 steps - or 19.8 rather than 20.
def stepAngle(self, direction, angle, speed =20, holdPosition=False, stepsPerRev=200):
steps = int(angle/(360/stepsPerRev))
print (steps)
self.step(direction, steps, speed, holdPosition)
#initialisation code for using:
#defaults to the standard pins and freq for the kitronik board, but could be overridden
def __init__(self,Motor1ForwardPin = machine.Pin(3),Motor1ReversePin = machine.Pin(2),Motor2ForwardPin = machine.Pin(6),Motor2ReversePin = machine.Pin(7),PWMFreq = 10000):
self.motor1Forward=machine.PWM(Motor1ForwardPin)
self.motor1Reverse=machine.PWM(Motor1ReversePin)
self.motor2Forward=machine.PWM(Motor2ForwardPin)
self.motor2Reverse=machine.PWM(Motor2ReversePin)
self.motor1Forward.freq(PWMFreq)
self.motor1Reverse.freq(PWMFreq)
self.motor2Forward.freq(PWMFreq)
self.motor2Reverse.freq(PWMFreq)
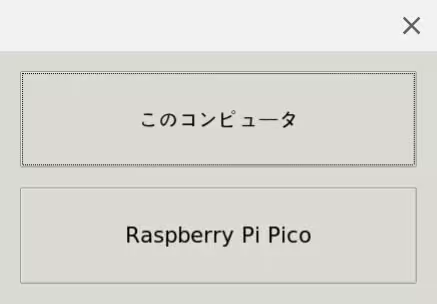
コードを保存する時は、Raspberry Pi Picoの方を選択して、マイコン内に直接保存します。
続いて、main.pyを作成します。
main.py
import PicoMotorDriver import time speed = 80 board = PicoMotorDriver.KitronikPicoMotor() board.motorOff(1) # 動作確認 board.motorOn(1, "f", speed) time.sleep(2) board.motorOn(1, "r", speed) time.sleep(2) board.motorOff(1)
今回はモータをforward(前進:時計回り)で2秒動かし、reverse(後進:半時計回り)で2秒動かした後に止めるという動作にしています。
コードを実行してみると、
のようになります。
- ラズベリーパイを使ってみる
- ラズベリーパイPico Wを使ってみる
- ラズベリーパイPico Wを初期化する
- ラズベリーパイPico WでLCDキャラクターディスプレイを使ってみる
- ラズベリーパイPico WでHTTPリクエストを送信してみる
- ラズベリーパイPico WでHTTPのPOSTで値を送信してみる
- ラズベリーパイPico WでHTTPのサーバを構築してみる
- ラズベリーパイPico WでHTTPリクエストでLEDを点灯できるようにしてみる
- ラズベリーパイPico Wでアクセスポイントを立ち上げLEDを点灯できるようにしてみる
- AndroidでラズベリーパイPico WからのHTTPリクエストを受信する
- ラズベリーパイPico WでBluetoothを使ってみる
- PythonでSerial Bluetooth Terminalの動作を再現してみる
- ラズベリーパイPico WでBluetoothのセントラル機器を構築してみる
- ラズベリーパイPico WでBluetooth接続を介してLチカをしてみる
- ラズベリーパイPico W同士をBluetooth接続してLチカをしてみる
- ラズベリーパイPico WとモータドライバでDCモータを動かしてみよう
- ラズベリーパイPico Wを介してブルートゥースでDCモータを制御してみよう
- ラズベリーパイPico W同士をブルートゥースで接続してDCモータを制御してみよう
- ラズベリーパイPico Wで270°サーボモータを動かしてみよう
- クロームブックでラズベリーパイとファイルの共有を行う
- シリアルコンソール経由でラズベリーパイを操作する
- LANケーブル経由でラズベリーパイを操作する
- クロームブックでFTP操作の代替のファイルアプリにマウントを利用する
- クロームブックでSFTPでファイルの転送を行う
- クロームブックで公開鍵認証でラズベリーパイにリモートアクセスする
- ラズベリーパイゼロ2W
- ラズベリーパイゼロ2Wにカメラモジュールを取り付ける
- ラズベリーパイゼロ2Wを動画ストリーミングサーバにしてみる
- ラズベリーパイのスワップを変更する
- ターミナルからラズベリーパイPicoにコードをフラッシングする
- ラズベリーパイで電源を入れた時に任意のアプリケーションを自動起動してみる
- ラズベリーパイPico WでGPS機能を設けてみる
- ラズベリーパイPico WでUARTを使ってみる